What would you like to export?
Do you want a report or the individual files?
What would you like to export?
Do you want a report or the individual files?
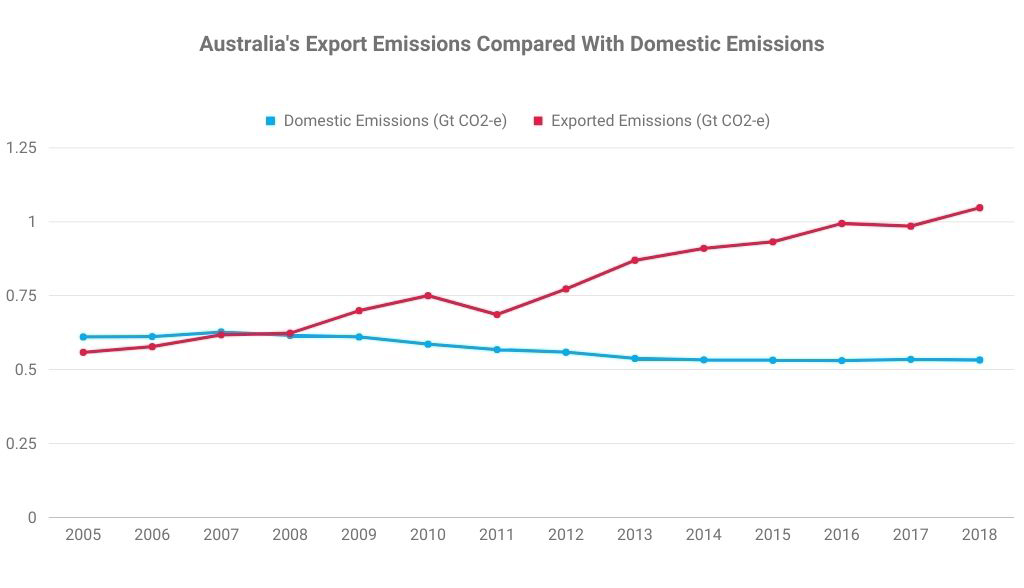
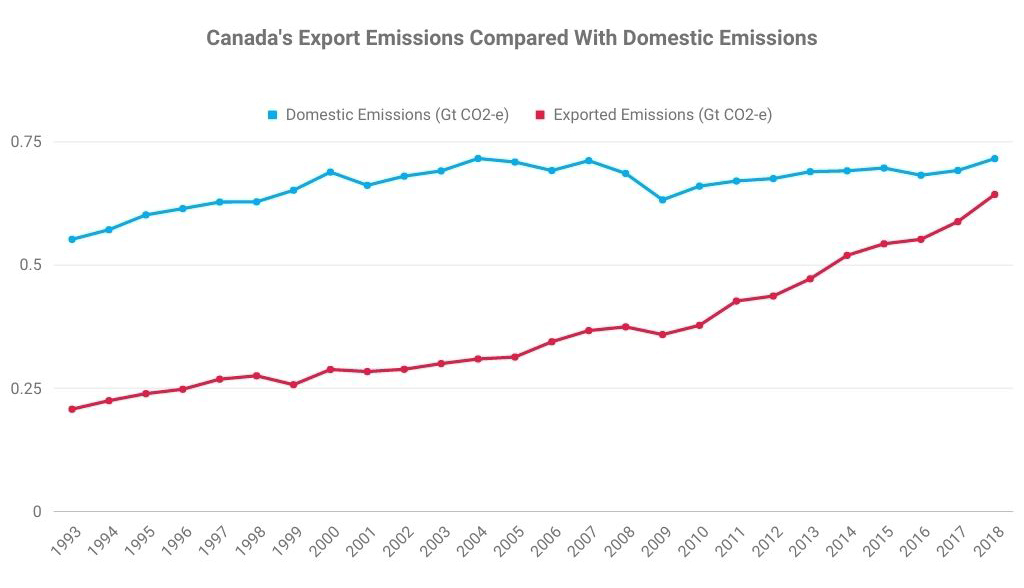
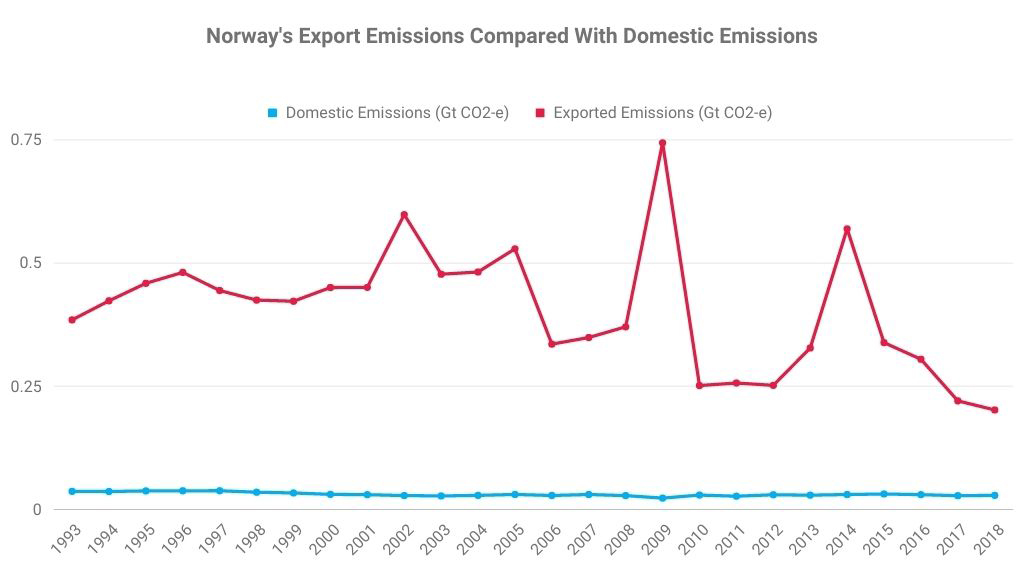
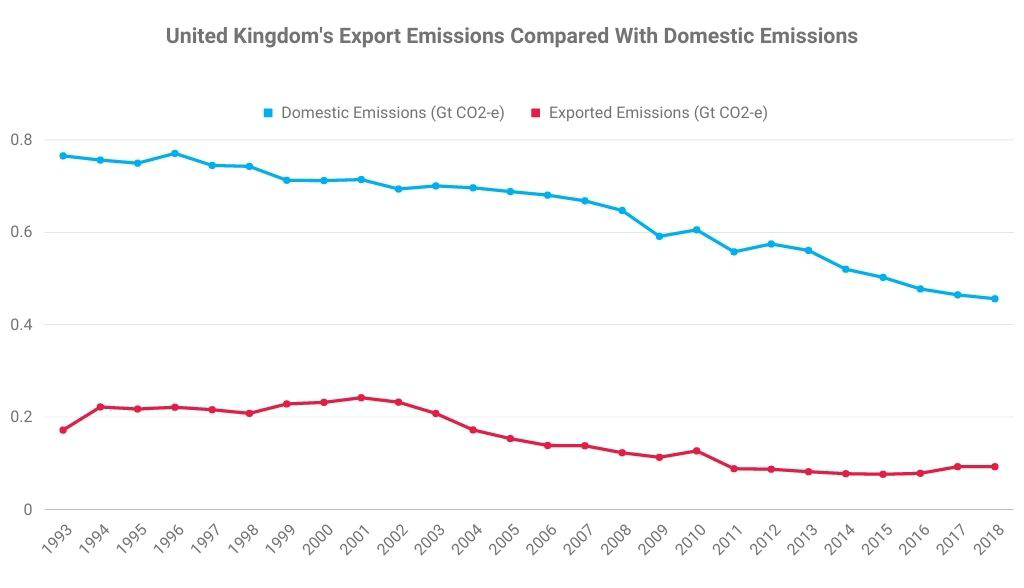
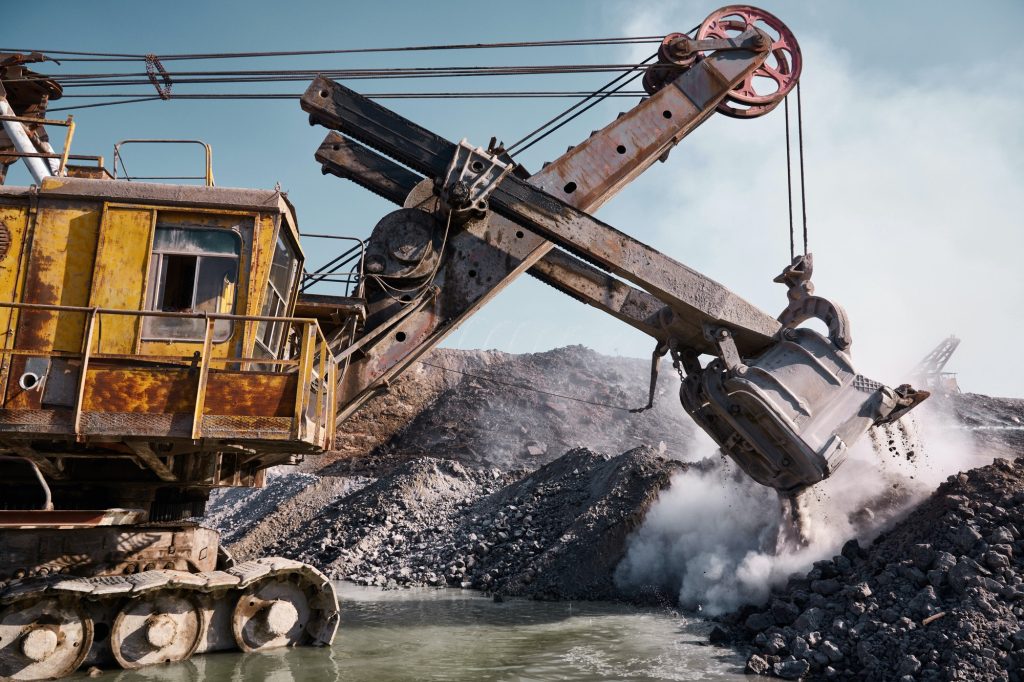
Metallurgical (met) coal (or coking coal) is a naturally occurring sedimentary rock found within the earth’s crust. Categories of met coal include hard coking coal, semi-hard coking-coal, semi-soft coking coal and pulverised coal for injection (PCI). These apply to the different quality grades of met coal, all of which are used to make steel. Met coal typically contains more carbon, less ash and less moisture than thermal coal, which is used for electricity generation.
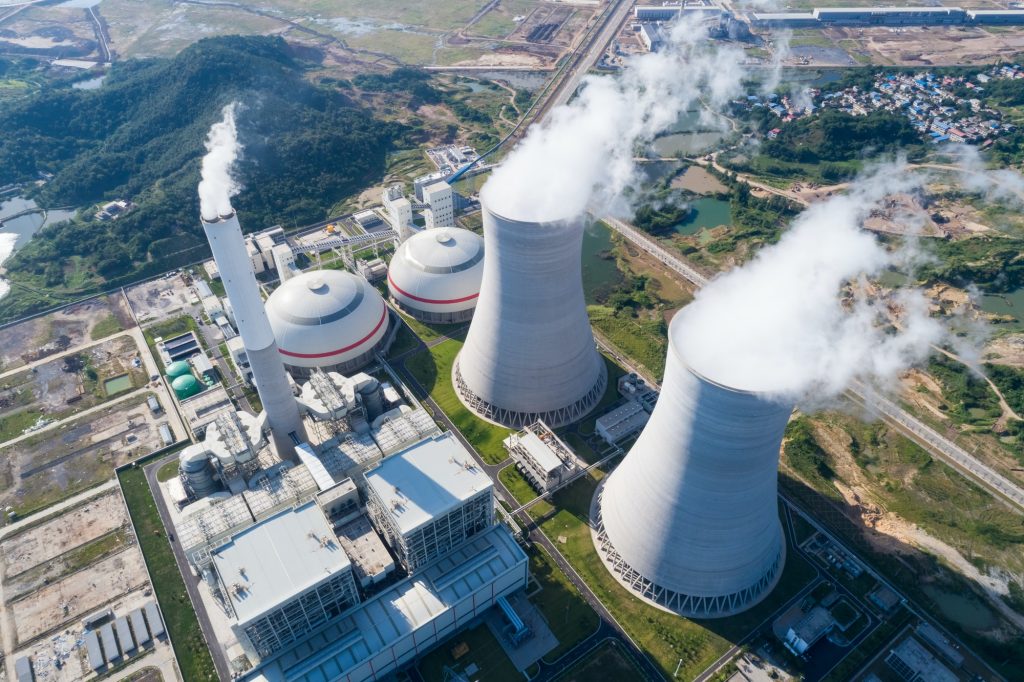


Thermal coal, also known as ‘steaming coal’ or just ‘coal’, is widely used as the principle means of generating electricity in much of the world. However, its high carbon and sulfur content means it is also a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions and global warming. This means it is increasingly being excluded from asset management portfolios, particularly those that seek to lower than carbon footprints.
Natural gas is a naturally occurring hydrocarbon gas mixture consisting of methane and commonly including varying amounts of other higher alkanes, and sometimes a small percentage of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide, or helium. Natural gas is colorless and odorless, and explosive, so a sulfur-smell (similar to rotten eggs) is usually added for early detection of leaks.
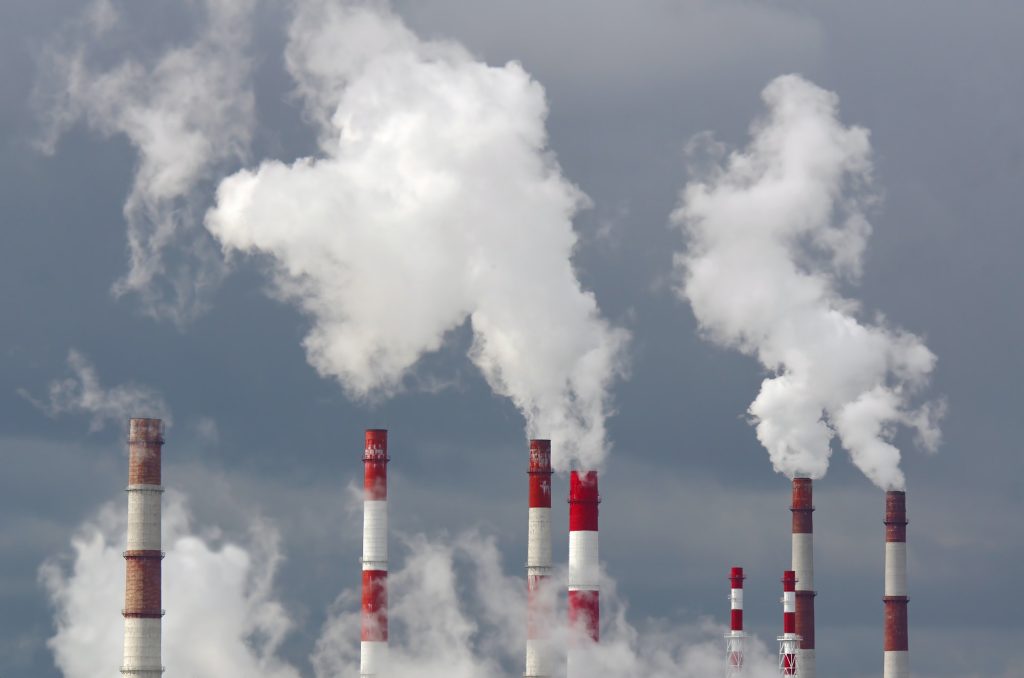
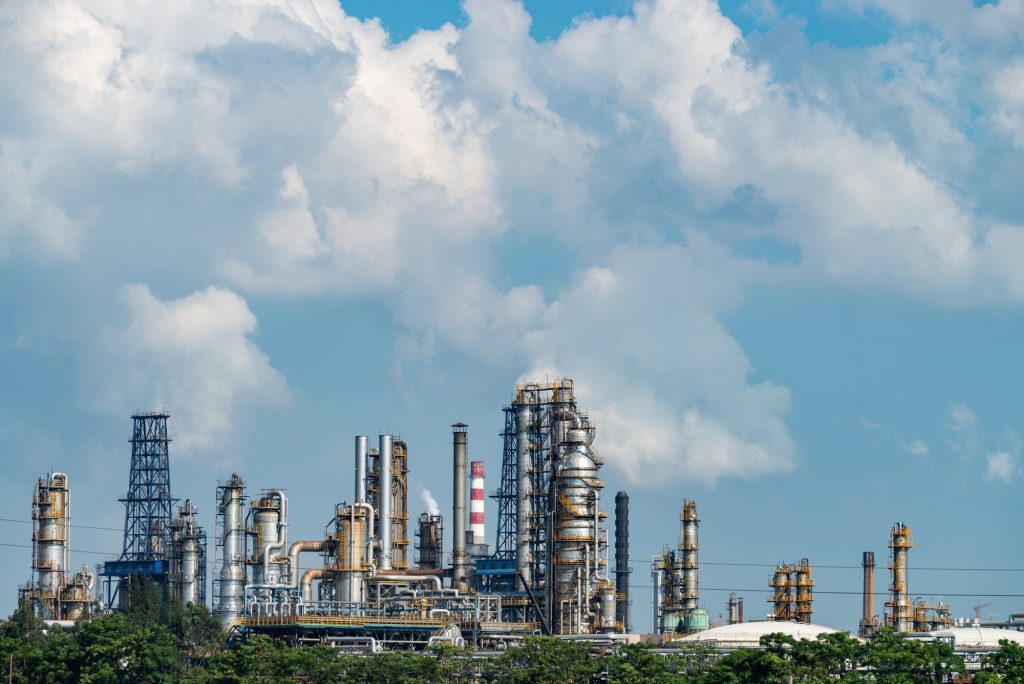


We call crude oil and petroleum fossil fuels because they are mixtures of hydrocarbons that formed from the remains of animals and plants (diatoms) that lived millions of years ago in a marine environment before the existence of dinosaurs. Over millions of years, the remains of these animals and plants were covered by layers of sand, silt, and rock.

Coal (metallurgical)
Coal (thermal)
Oil
Gas